Dynamic (absolute) Viscosity
Newton's law of viscosity states that the shearing stress and the rate of deformation are directly proportional through a constant of proportionality called viscosity, τ = μ du/dy, where
.svg/655px-Pythagorean_proof_(1).svg.png)
= 1 Pa-s = 47.8803 Pa-s = 1.48816 Pa-s = 17.858 Pa-s = 6894.76 Pa-s = 47.8803 Pa-s = 574.563 Pa-s - centipoise - dyne second per square centimeter - gram force second per square centimeter - gram per centimeter per second - kilogram force second per square meter - kilogram per meter per second - newton second per square meter - pascal second. Viscosity is the measurement of a fluid's internal resistance to flow. This is typically designated in units of centipoise or poise but can be expressed in other acceptable measurements as well. Some conversion factors are as follows: 100 Centipoise = 1 Poise 1 Centipoise = 1 mPa s (Millipascal Second) 1 Poise = 0.1 Pa s (Pascal Second). Pascal-second (symbol: Pa.s) + milliPascal-second (symbol: mPa.s) This is the SI unit of viscosity, equivalent to newton-second per square metre (Ns m–2). It is sometimes referred to as the poiseuille (symbol Pl). One poise is exactly 0.1 Pas. One poiseuille is 10 poise or 1000 cP, while 1 cP = 1 mPas (one millipascal-second). Poiseuille (Pa s) Poise (dyne s/cm 2, g/cm s) centiPoise kg/m h kg f s/m 2 lb f s/inch 2 lb f s/ft 2 lb f h/ft 2 lb/ft s lb/ft h A Dynamic or Absolute Viscosity Units Converting Table The table below can be used to convert between common dynamic or absolute viscosity units. Viscosity of Aqueous Glycerine Solutions in Centipoises/mPa s Temperatur e (ϒC)Glycerine percent weight 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 0 (1) 1.792 1.308 1.005 0.8007 0.6560 0.5494 0.4688 0.4061 0.3565 0.3165 0.2838.
Mpa-s To Poise
μ = dynamic viscosity - N·s/m²
du/dy = velocity gradient at y direction - 1/s
The dynamic viscosity units are N·s/m², Pa·s or kg/m·s, where
In the metric centimeter-gram-second system, the dynamic viscosity units can also be expressed as g/cm·s, dyne.s/cm² or poise (p) where

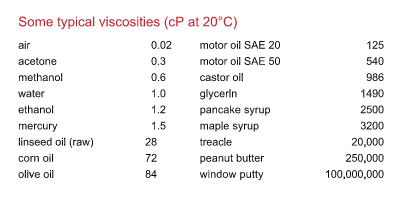
In the industry of petroleum, centiPoise (cP) or milliPascal-second (mPa·s) is offen used as the unit of dynamic viscosity.
Kinematic Viscosity

The ratio of dynamic viscosity to density of the fluid is the kinematic voscosity, ν = μ / ρ, where
μ = dynamic viscosity - 1 N·s/m² or kg/m·s
ρ = density - kg/m³
Mpa To Cst Conversion
SI uses Stokes (St) as the unit of kinematic viscosity. 1 Stokes (St) is the kinematic viscosity of a fluid with dynamic viscosity of one P and volumic mass 1 g/cm³.
Another frequent used unit of kinematic viscosity is Centistokes (cSt). 1 Centistokes (cSt) is the kinematic viscosity of a fluid with dynamic viscosity of 1 cP and volumic mass 1 g/cm³.
1 cSt = 10-6 m²/s = 1 mm²/s
Viscosity Mpa To Centipoise
Saybolt Universal Viscosity
Mpa To Cps
The efflux time in seconds of 60 ml of fluid flowing though a calibrated Universal orifice under the coditions prescribed by test method ASTM D 88, is the Saybolt Universal Viscosity reported as Saybolt Universal Seconds (SUS) at a specified temperature.
